- The Pap test, also called a Pap smear, checks for changes to the cells on a woman's cervix. (The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina.
- A Pap test can detect infections, precancerous cells, or cervical cancer, which can usually be treated successfully if caught early.
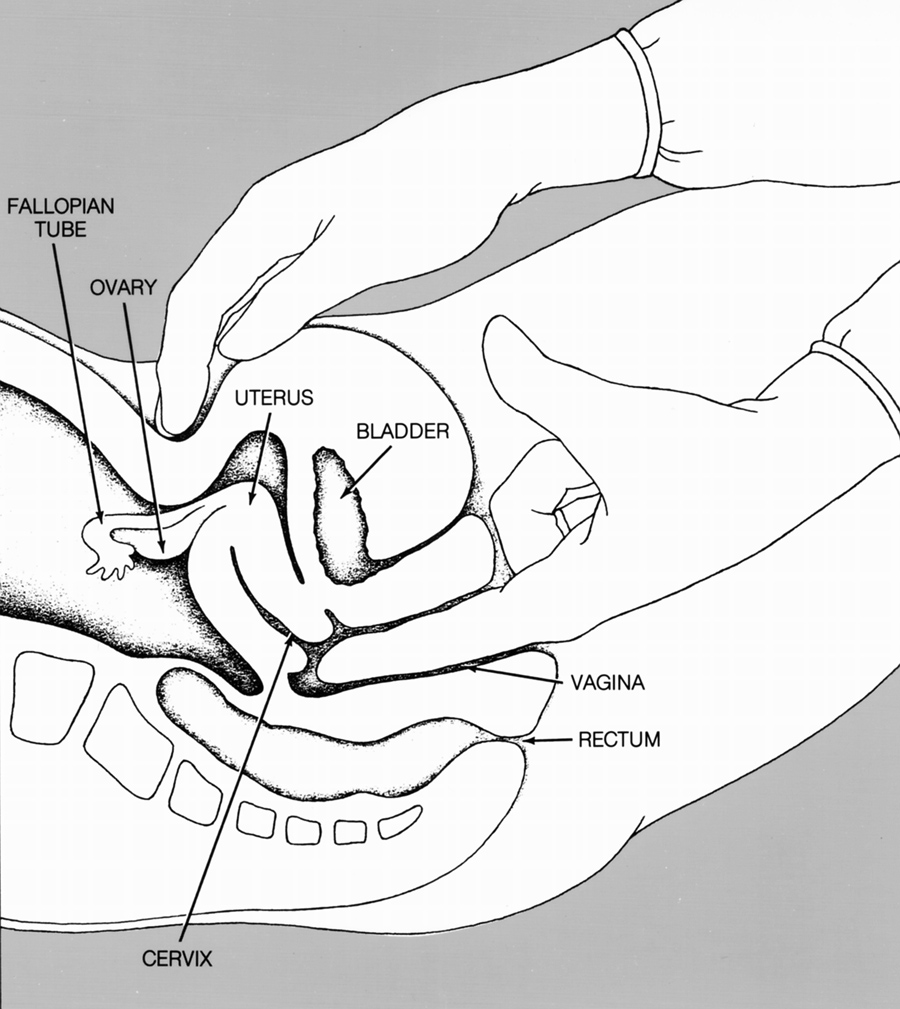
- A Pap test is usually done during a pelvic exam.
- Avoid douching, using tampons, vaginal creams, vaginal suppositories, vaginal medicines, vaginal deodorant products, or having sex for two days before your Pap test.
- The best time to be tested is 10-20 days after the first day of your last period.
- There are many reasons for an abnormal Pap test. Abnormal results don't always indicate something serious like cancer.
- Abnormal cells found from a Pap test can sometimes be treated to prevent cervical cancer.
- For abnormal results that do indicate serious changes in your cervix, your doctor may perform additional tests, such as colposcopy, endocervical curettage, or biopsy.
- Some Pap tests yield a false positive or false negative result. Having regular Pap tests increases the chances of finding a problem, because if abnormal cells are missed at one time, they will probably be found on your next Pap test.
Why should a woman have a Pap test?
Pap tests can save lives. It can find the earliest signs of cervical cancer. When diagnosed in its early stages, cervical cancer cure rates are very high.
Pap tests also can find infections and abnormal cervical cells that can turn into cancer cells. Treatment can prevent most cases of cervical cancer from developing.
Getting regular Pap tests is the best thing you can do to prevent cervical cancer. In fact, regular Pap tests have led to a major decline in the number of cervical cancer cases and deaths.
How is a Pap test done?
Your doctor can do a Pap test during a pelvic exam. It is a simple and quick test. While you lie on an exam table, the doctor puts an instrument called a speculum into your vagina, opening it to see the cervix. She will then use a special swab or brush to take a few cells from inside and around the cervix. The cells are placed on a glass slide and sent to a lab for examination. While usually painless, a Pap test is uncomfortable for some women.
How often does a woman need to get a Pap test?
It is important for all women to have Pap tests, along with pelvic exams, as part of their routine health care. You need a Pap test if you are 21 years or older.
The frequency of testing will depend on a woman's age and medical history. Most women can follow these guidelines:
- Starting at age 21, have a Pap test every 2 years.
- If you are 30 years old and older and have had 3 normal Pap tests for 3 years in a row, talk to your doctor about spacing out Pap tests to every 3 years.
- If you are over 65 years old, ask your doctor if you can stop having Pap tests.
Women who have gone through menopause (when a woman's periods stop) still need regular Pap tests. Women ages 65 and older can talk to their doctor about stopping after at least 3 normal Pap tests and no abnormal results in the last 10 years.
Ask your doctor about more frequent testing if:
- You have a weakened immune system because of organ transplant, chemotherapy, or steroid use
- Your mother was exposed to diethylstilbestrol (DES) while pregnant
- You are HIV-positive
Women who are living with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, are at a higher risk of cervical cancer and other cervical diseases.
Women who have had a hysterectomy should talk with their doctor about whether they need routine Pap tests.
What is required before a Pap test?
Doctors suggest you schedule a Pap test when you do not have your period. The best time to be tested is 10 to 20 days after the first day of your last period.
Many things can cause wrong test results by washing away or hiding abnormal cells of the cervix. 2 days before the Pap test you avoid the following:
- Douching
- Using tampons
- Using vaginal creams, suppositories, and medicines
- Using vaginal deodorant sprays or powders
- Having sex
What do abnormal Pap test results mean?
It is scary to hear that your Pap test results are "abnormal." But abnormal Pap test results usually do not mean you have cancer. Most often there is a small problem with the cervix.
Some abnormal cells will turn into cancer. For instance, infection with the HPV virus can increase the likelihood that cervical cells will become cancerous. However, these unhealthy cells will usually go away on their own. By treating these unhealthy cells, almost all cases of cervical cancer can be prevented.
If you have abnormal results, to talk with your doctor about what they mean.
My Pap test was "abnormal." What happens now?
There are many reasons for "abnormal" Pap test results. If results of the Pap test are unclear or show a small change in the cells of the cervix, your doctor will probably repeat the Pap test.
If the test finds more serious changes in the cells of the cervix, the doctor will suggest more powerful tests. Results of these tests will help your doctor decide on the best treatment. These include:
- Colposcopy: The doctor uses a tool called a colposcope to see the cells of the vagina and cervix in detail.
- Endocervical curettage: The doctor takes a sample of cells from the endocervical canal with a small spoon-shaped tool called a curette.
- Biopsy: The doctor removes a small sample of cervical tissue. The sample is sent to a lab to be studied under a microscope.
My Pap test result was a "false positive." What does this mean?
Pap tests are not always 100% correct. False positive and false negative results can happen. This can be upsetting and confusing. A false positive Pap test is when a woman is told she has abnormal cervical cells, but the cells are really normal. If your doctor says your Pap results were a false positive, there is no problem.
A false negative Pap test is when a woman is told her cells are normal, but in fact, there is a problem with the cervical cells that was missed. False negatives delay the discovery and treatment of unhealthy cells of the cervix. But, having regular Pap tests boosts your chances of finding any problems. If abnormal cells are missed at one time, they will probably be found on your next Pap test.
Source: Vivacare
Last updated : 1/8/2019